Difference between RS232 and RS485
RS232 and RS485 are parts of communication protocol, lets know the definition of those types.
What is RS485 protocol?
The most common serial interface in industry is the RS485 or EIA-485 protocol. This interface provides a considerable advantage over RS232 connections. Using multi-point topology, several receivers and transmitters may be connected. Data is delivered through differential signals for increased consistency.
There are two ways to communicate with RS485:
RS485 connections with two contacts operate in half-duplex mode, which limits the amount of simultaneous data transmission and reception.
Up to four contacts can be present on an RS485 connection, enabling full-duplex operation. When used in this way, data may be delivered and received at the same time.
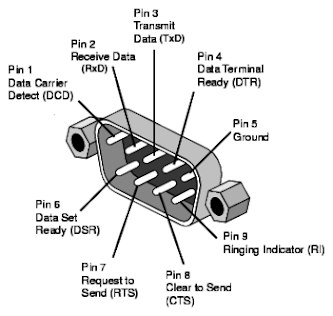
TIA/EIA-232, sometimes referred to as the RS232 interface, is a serial communication control protocol. It arranges the flow of data from a Data Terminal Equipment (DTE), such as a transmitter or terminal, to a receiver or other type of Data Communications Equipment (DCE).
The distance between the devices directly affects how quickly information is sent. Serial communication can be established in full-duplex or half-duplex modes. Full-duplex enables simultaneous delivery and receipt of data by using separate lines for transmission and reception. In a half-duplex system, only one line is used for data transmission and reception, which leads to more constrained functionality. Half-duplex allows for simultaneous data transmission or reception, but not both.
What is the difference between RS232 and RS485 serial ports?
Two electrical transmission protocols that before the development of personal computers are RS232 and RS485. In serial communication interfaces between computers and peripheral devices, they are utilised. Despite the fact that they both support serial data transport, the RS232 and RS485 protocols have considerable differences. Let's examine the distinctions between these approaches.
The main difference between RS232 and RS485 serial ports are in:
Mode of operation
Distant communication
Amounts of voltage
How many contacts are now active, etc.
So let's take a closer look at these distinctions.
The quantity of wires Although some connections have up to 25 wires, an RS232 cable typically contains nine wires. Each cable plays a certain function during the data transfer. In RS485 cables, there are just three wires total: two for data transmission and one for grounding.
Full-duplex transmission - RS232 is capable of sending and receiving data in both directions. Bidirectional RS485 connection necessitates the use of an additional pair of cables. By default, RS485 is half-duplex, which limits the amount of data that can be sent at once.
The voltage range for RS485 is +5V to -5V. Although signals can degrade to as low as 3V, the ideal voltage range for RS232 is +12V to -12V. Range: There are substantial differences between the maximum cable lengths that may be used with the RS232 and RS485 protocols. The maximum length of an RS232 cable is normally 50 feet (15 metres). The maximum length of an RS485 cable is 4,000 feet (1,200 m).
The distinctions between these two methods may occasionally favour one answer over the other. The simultaneous use of both protocols is made possible by the existence of RS232 to RS485 converters. In most cases, these converters are bidirectional, enabling connections from RS232 to RS485 as well as from RS485 to RS232.
Where is the serial data transmission protocol used?
Since USB and other protocols have replaced them, serial data transmission via the RS232 or RS485 protocols is no longer the industry standard for consumer computers and electrical peripherals. Serial transmission is still often used in embedded systems and industrial monitoring, and it may be used with USB-equipped devices by employing adapters.
RS232 offers direct administration of industrial equipment, such as UPS systems, without the need for software. Many industrial sensors and monitors in the Industrial Internet of Things employ serial connectivity. It's a common option for scientific and medical equipment as well. A lot of CCTV (Closed Circuit Television) cameras use the RS485 protocol.
Advantages and disadvantages of RS232
RS485 (Multiple Drive Communications)
The RS485 standard is analogous to the RS422 standard it is built on. The main difference is that up to 32 transmitter-receiver pairs can be present on the RS485 lines at the same time. A typical RS-485 system is a two-wire half-duplex system. The RS485 4-wire full duplex system is quite similar to the RS-422 system.
The RS485 protocol is still in widespread usage. It is similar to the RS422, on which it is based. The RS485 port has been in use for many years. When it comes to applications in noisy industrial environments, RS485 outperforms both RS232 and USB. RS422 devices can be used as receivers only on an RS485 bus network.
The Primary features of RS-485 are:
Standard of RS485
- Up to 32 Driver/Receiver Pairs
- Line Length Max Data Rate
- 40 Feet = 12m 10 Mbits/sec
- 400 Feet = 122m 1 Mbits/sec
- 4000 Feet = 1219m 100 kbits/sec
Termination resistor
Termination resistors should be fitted at both ends of the twisted pair of wires. The impedance value should be the same as the characteristic impedance of the twisted pair, and it should be put at both ends of the cable. A termination resistor is not required for cables of less than 2000 feet with baud rates of 9600bps or below.
If a termination resister is required, it should be 120 ohms or above. Only two termination resistors, one at each end of the RS485 transmission line, should be used.
At all times, the A and B wires should be looped together. When electrical, magnetic, and RF noise couple onto the A B cable, looping the cable uniformly distributes the noise across both A and B wires, resulting in no differential noise in the differential data.














0 Comments