Explanation of the specifications of the plate capacitors to improve the capacity factor:
From the previous lectures and will be linked to this lecture, we learned that electrical energy is divided into three types:
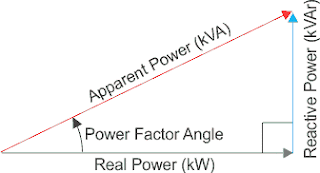
Apparent power: It is symbolized by the symbol S and measured as KVA, which is the vector sum of the active and passive power, i.e. the total power used. As a factory or company, the electrical loads are drawn from Active Power - Reactive Power, according to the value of the need for each of them. The power factor, which is symbolized by the symbol PF or CosФ, is determined, so we find that:
P.F = Active Power /Apparent Power, and its value ranges from 0 to 1.
From here we can know the power factor as the ratio between the effective power to the apparent power, in the local sense (effective power is what of the apparent power). Of course, the effective power is fixed and all play in the apparent power by controlling the ineffective power.
Reasons for improving the power factor: There are many advantages to developing the power factor, including:
Improving the efficiency of devices in various electrical systems.
Reduce the voltage drop.
Increase the available capacity.
Use of capacitors:
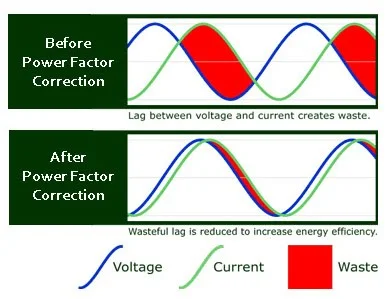
Electrical capacitors, especially fixed ones, are used to withdraw the delayed electric current due to the presence of excessive electrical loads. Therefore, electrical capacitors are installed in parallel with electrical loads with a low power factor, to correct the value of the lag in the current in the circuit. The use of these capacitors is characterized by being : Light weight. It is easy to install, and it has some drawbacks that should be noted that it has a short lifespan of about 10 years, and it is considered high cost when you need to replace it due to its damage.
The installation of a capacitor with inductive loads in the same circuit leads to an exchange of current between them in such a way that the leading current (leading current) drawn by the capacitor is equivalent to a portion of the lagging current of the inductive loads necessary for magnetization, so the capacitor is the primary management that is used to improve the power factor
Modify the power factor:
The power factor is adjusted and raised to reduce the consumption of reactive power by installing capacitors in parallel with the load to provide the required reactive power for the electrical loads. The capacitor is the most practical and economical device to improve it, as we mentioned the reactive power or inductive power produces from inductive loads loads .
Capacitors produce a power that is completely opposite to it, and it vanishes, and it is called capacitive reactive power, to prevent the flow of ineffective current in the lines between the load and the power station. The capacitor is connected in parallel with the load as a storage device for the inactive current. The reactive current when the load is connected does not return to the power station but rather to the capacitor and circulates between the capacitor and the load.





0 Comments