Positive Displacement Pump
What is the Positive Displacement Pump?
A positive displacement pump can be further categorized based on the fluid-moving mechanism:
- Rotary-type positive displacement pump
The fluid is transported by a rotating component of this pump. The fluid is displaced from the reservoir to the discharge pipe due to spinning. Internal gear, screw pump, flexible vane or sliding vane, flexible impeller, circumferential pump, helical twisted roots, and other examples of these sorts of pumps are widespread.
There are three main types of rotary positive displacement pumps:
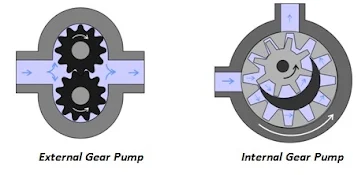
- Gear Pump: Fluid is transferred between two spinning gears in this pump. As the liquid turns, it is forced between these two gears.
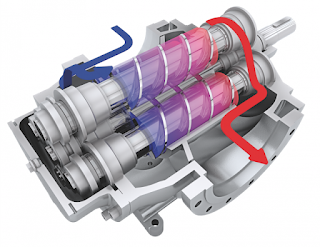
- Screw Pump: Two screw-type rotors revolve against each other in these pumps. The water is sucked from the intake and pumped to the output as the two screws revolve.
 |
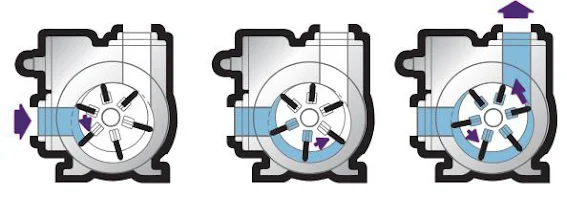
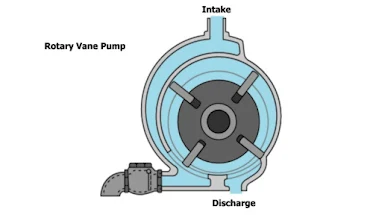
- Rotary Vane Pump: Scroll compressors are comparable to this. It is made up of a cylindrical rotor with vanes on it that is housed in a cylindrically formed casing. The vanes on the rotor trap the fluid between the rotor and the casing and discharge it via the outlet as it rotates.
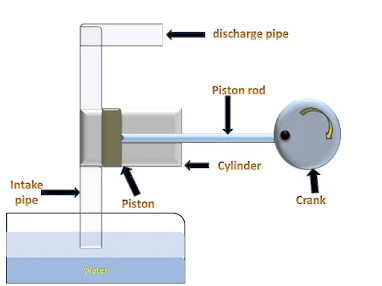
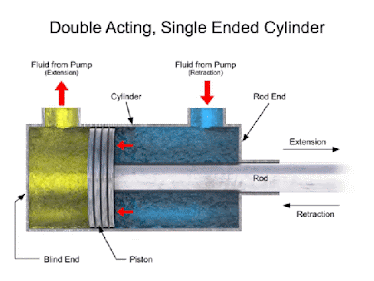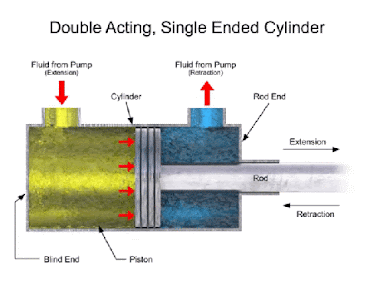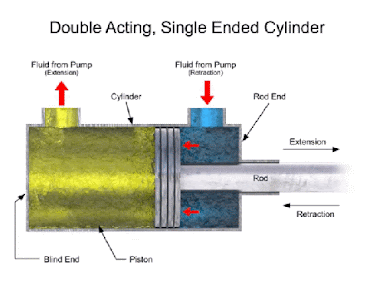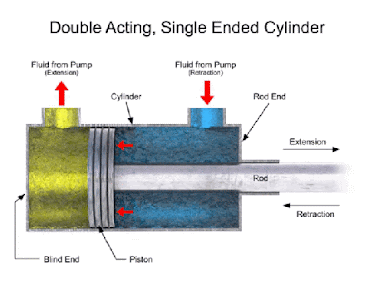
- Reciprocating-type positive displacement pump
A reciprocating component (which travels back and forth) pumps the water in these pumps. Plunger, piston, or diaphragm reciprocating components are possible. There are valves, inlet valves, and exit valves in it. During liquid suction, the intake valves open and the exit valves close. During liquid discharge, inlet valves stay closed while exit valves open.
- The input cavity of some reciprocating pumps expands while the output cavity shrinks. As the hollow grows, the liquid is drawn in and discharged as the cavity shrinks.
- The categories of reciprocating pumps range from basic (one cylinder) to quad (four) or even more. Duplex (two) or triplex (three) cylinders are found in most of their models.
- It can be operated manually, with steam or air, or with an engine-driven belt.
- It was most often employed as a boiler feed water pump in the nineteenth century. It is now used to pump very viscous fluids such as heavy oils and concrete, as well as in specific applications requiring fluid to flow at low rates against considerable resistance.






0 Comments